NumPy: array() function
array() function
The array() function is used to create an array.
Syntax:
numpy.array(object, dtype=None, copy=True, order=’K’, subok=False, ndmin=0)
Version: 1.15.0
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| object | An array, any object exposing the array interface, an object whose __array__ method returns an array, or any (nested) sequence. | Required | |||||||||||||||
| dtype | The desired data-type for the array. If not given, then the type will be determined as the minimum type required to hold the objects in the sequence. This argument can only be used to 'upcast' the array. For downcasting, use the .astype(t) method. | optional | |||||||||||||||
| copy | If true (default), then the object is copied. Otherwise, a copy will only be made if __array__ returns a copy, if obj is a nested sequence, or if a copy is needed to satisfy any of the other requirements (dtype, order, etc.). | optional | |||||||||||||||
| order | Specify the memory layout of the array. If object is not
an array, the newly created array will be in C order (row major) unless ‘F’ is specified, in
which case it will be in Fortran order (column major). If object is an array the following holds.
When copy=False and a copy is made for other reasons, the result is the same as if copy=True, with some exceptions for A, see the Notes section. The default order is ‘K’. |
optional | |||||||||||||||
| subok | If True, then sub-classes will be passed-through, otherwise the returned array will be forced to be a base-class array (default). | optional | |||||||||||||||
| ndmin | Specifies the minimum number of dimensions that the resulting array should have. Ones will be pre-pended to the shape as needed to meet this requirement | optional |
Return value:
[ndarray] An array object satisfying the specified requirements
Example -1: numpy.array(0 function
>>> import numpy as np
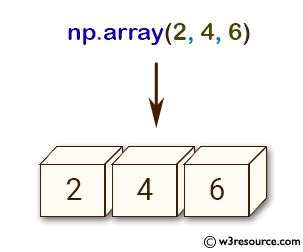
>>> np.array([2, 4, 6])
array([2, 4, 6])
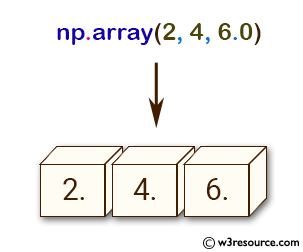
>>> np.array([2, 4, 6.0])
array([ 2., 4., 6.])
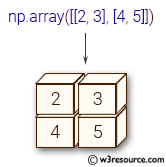
>>> np.array([[2, 3], [4, 5]])
array([[2, 3],
[4, 5]])
Pictorial Presentation:
Example-2: numpy.ones_like() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.array([(2,4),(5,6)], dtype=[('x', '<i4'), ('y','i4')])
>>> a['y']
array([4, 6], dtype=int32)
>>> a['x']
array([2, 5], dtype=int32)
Example-3: numpy.ones_like() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.array(np.mat('2, 4; 5, 6'))
array([[2, 4],
[5, 6]])
>>> np.array(np.mat('2 4; 6 8'))
array([[2, 4],
[6, 8]])
Example-4: numpy.ones_like() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.array([2, 4, 6], ndmin=4)
array([[[[2, 4, 6]]]])
Example-4: numpy.ones_like() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.array(np.mat('2 4; 6 8'), subok=True )
matrix([[2, 4],
[6, 8]])
>>> np.array(np.mat('2 4; 6 8'), subok=False)
array([[2, 4],
[6, 8]])
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: full_like()
Next: asarray()
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
