NumPy: reshape() function
numpy.reshape() function
The reshape() function is used to give a new shape to an array without changing its data.
Syntax:
numpy.reshape(a, newshape, order='C')
Version: 1.15.0
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| a | Array to be reshaped. | Required |
| newshape | The new shape should be compatible with the original shape. If an integer, then the result will be a 1-D array of that length. One shape dimension can be -1. In this case, the value is inferred from the length of the array and remaining dimensions. | Required |
| order | Read the elements of a using this index order, and place the elements into the reshaped array using this index order. ‘C’ means to read / write the elements using C-like index order, with the last axis index changing fastest, back to the first axis index changing slowest. ‘F’ means to read / write the elements using Fortran-like index order, with the first index changing fastest, and the last index changing slowest. Note that the ‘C’ and ‘F’ options take no account of the memory layout of the underlying array, and only refer to the order of indexing. ‘A’ means to read / write the elements in Fortran-like index order if a is Fortran contiguous in memory, C-like order otherwise. | Optional |
Return value:
reshaped_array : ndarray - This will be a new view object if possible; otherwise, it will be a copy. Note there is no guarantee of the memory layout (C- or Fortran- contiguous) of the returned array.
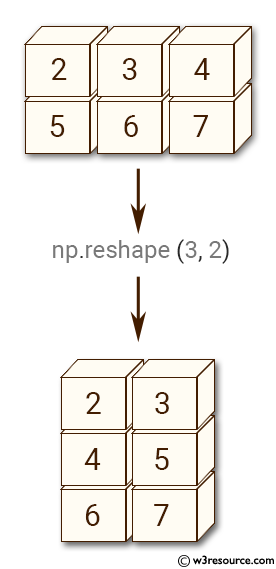
Example-1: numpy.reshape() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[2,3,4], [5,6,7]])
>> np.reshape(x, (3, 2))
array([[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7]])
Pictorial Presentation:
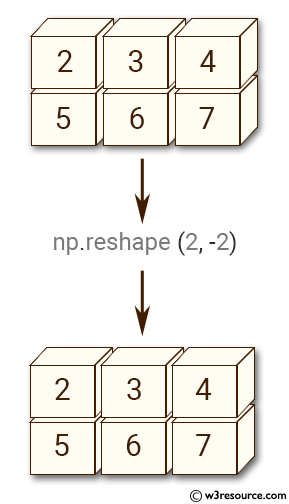
Example-2: numpy.reshape() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[2,3,4], [5,6,7]])
>>> np.reshape(x, (2, -2))
array([[2, 3, 4],
[5, 6, 7]])
Pictorial Presentation:
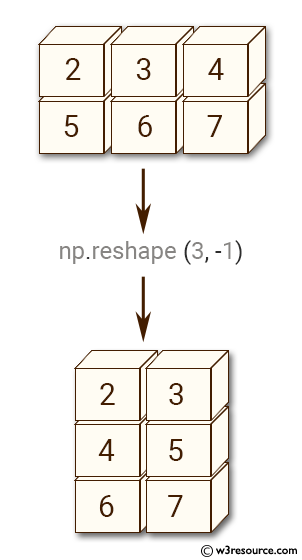
Example-3: numpy.reshape() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[2,3,4], [5,6,7]])
>>> np.reshape(x, (3, -1))
array([[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7]])
Pictorial Presentation:
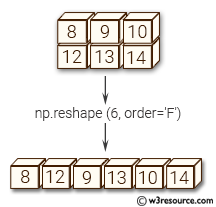
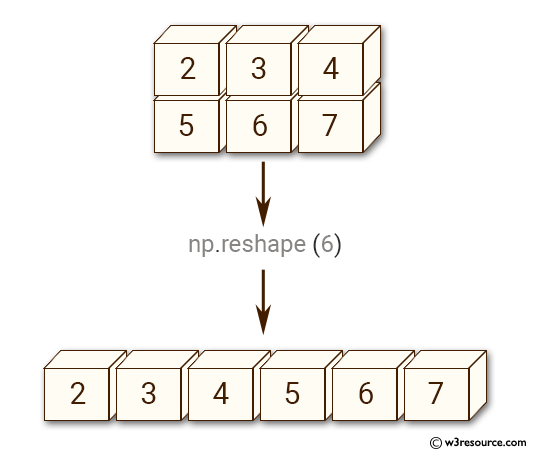
Example-4: numpy.reshape() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[2,3,4], [5,6,7]])
>>> np.reshape(x, 6)
array([2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7])
Pictorial Presentation:
Example-5: numpy.reshape() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[2,3,4], [5,6,7]])
>>> np.reshape(x, 6, order='F')
array([2, 5, 3, 6, 4, 7])
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
