NumPy: dstack() function
numpy.dstack() function
The dstack() is used to stack arrays in sequence depth wise (along third axis).
This is equivalent to concatenation along the third axis after 2-D arrays of shape (M,N) have been reshaped to (M,N,1) and 1-D arrays of shape (N,) have been reshaped to (1,N,1). Rebuilds arrays divided by dsplit.
This function makes most sense for arrays with up to 3 dimensions. For instance, for pixel-data with a height (first axis), width (second axis), and r/g/b channels (third axis). The functions concatenate, stack and block provide more general stacking and concatenation operations.
Syntax:
numpy.dstack(tup)
Version: 1.15.0
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| tup | The arrays must have the same shape along all but the third axis. 1-D or 2-D arrays must have the same shape. | Required |
Return value:
stacked : ndarray The array formed by stacking the given arrays, will be at least 3-D.
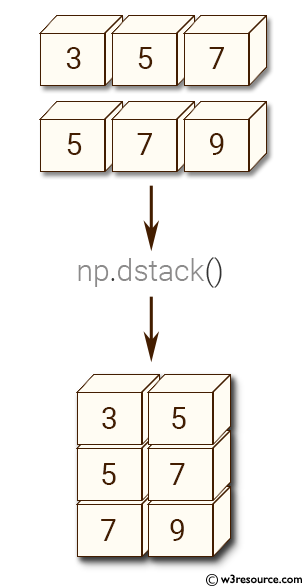
Example-1: numpy.dstack()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array((3, 5, 7))
>>> y = np.array((5, 7, 9))
>>> np.dstack((x,y))
array([[[3, 5],
[5, 7],
[7, 9]]])
Pictorial Presentation:
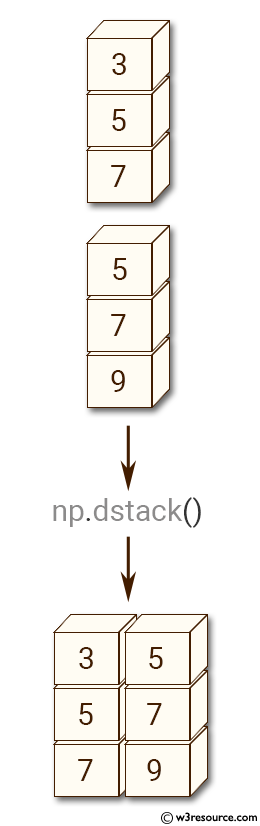
Example-2: numpy.dstack()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.array([[3], [5], [7]])
>>> y = np.array([[5], [7], [9]])
>>> np.dstack((x,y))
array([[[3, 5]],
[[5, 7]],
[[7, 9]]])
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: column_stack()
Next: hstack()
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
