NumPy: delete() function
numpy.delete() function
The delete() function returns a new array with sub-arrays along an axis deleted. For a one dimensional array, this returns those entries not returned by arr[obj].
Syntax:
numpy.delete(arr, obj, axis=None)
Version: 1.15.0
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| arr | Input array. | Required |
| obj | Indicate which sub-arrays to remove. | Required |
| axis | The axis along which to delete the subarray defined by obj. If axis is None, obj is applied to the flattened array. | Optional |
Return value:
[ndarray] A copy of arr with the elements specified by obj removed. Note that delete does not occur in-place. If axis is None, out is a flattened array.
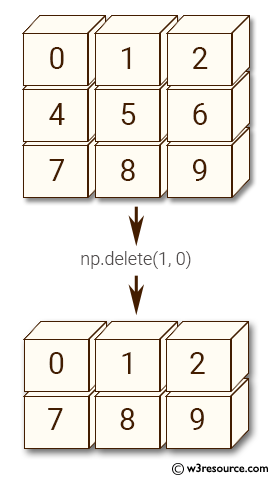
Example-1: numpy.delete()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> arr = np.array([[0,1,2], [4,5,6], [7,8,9]])
>>> arr
array([[0, 1, 2],
[4, 5, 6],
[7, 8, 9]])
>>> np.delete(arr, 1, 0)
array([[0, 1, 2],
[7, 8, 9]])
Pictorial Presentation:
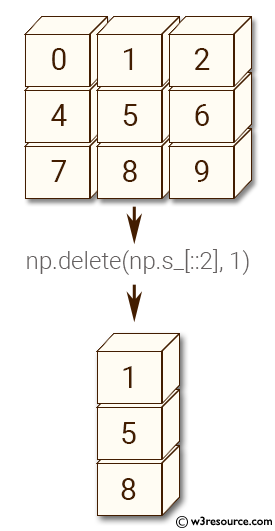
Example-2: numpy.delete()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.delete(arr, np.s_[::2], 1)
array([[1],
[5],
[8]])
>>> np.delete(arr, [1, 2, 5], None)
array([0, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9])
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
