NumPy: append() function
numpy.append() function
The append() function is used to append values to the end of an given array.
Syntax:
numpy.append(arr, values, axis=None)
Version: 1.15.0
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| arr | Values are appended to a copy of this array. | Required |
| values | These values are appended to a copy of arr. It must be of the correct shape (the same shape as arr, excluding axis). If axis is not specified, values can be any shape and will be flattened before use. | Required |
| axis | The axis along which values are appended. If axis is not given, both arr and values are flattened before use. | Optional |
Return value:
append : ndarray - A copy of arr with values appended to axis. Note that append does not occur in-place: a new array is allocated and filled. If axis is None, out is a flattened array.
Example-1: numpy.append()
>>> import numpy as np
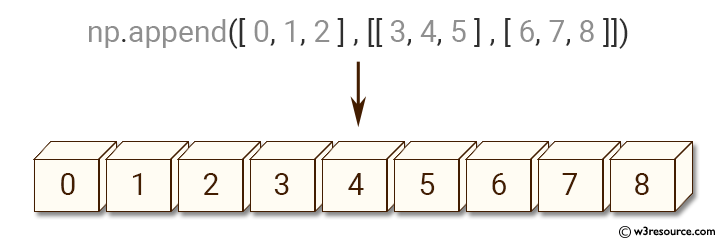
>>> np.append ([0, 1, 2], [[3, 4, 5], [6, 7, 8]])
array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8])
Pictorial Presentation:
Example-2: numpy.append()
>>> import numpy as np
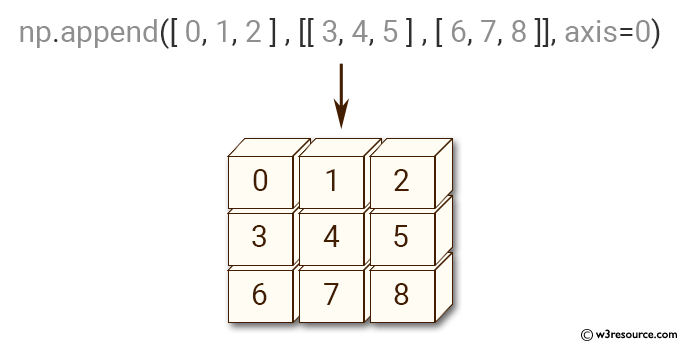
>>> np.append([[0, 1, 2], [3, 4, 5]],[[6, 7, 8]], axis=0)
array([[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8]])
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
