SQL MOD() function
MOD() function
SQL MOD() function is used to get the remainder from a division. The SQL DISTINCT command along with the SQL MOD() function is used to retrieve only unique records depending on the specified column or expression.
Syntax:
MOD( dividend, divider )
PostgreSQL and Oracle
All of above platforms support the SQL syntax of MOD().
MySQL Syntax:
MOD(dividend,divider); dividend % divider; dividend MOD divider;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| dividend | A number. |
| divider | A number. |
SQL MOD() function: Pictorial presentation
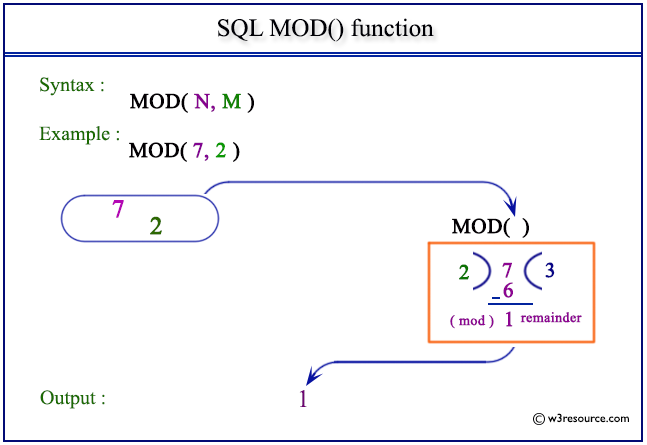
Example:
To get remainder of a division of 25 by 7 from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT MOD(25,7)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(25,7)
----------
4
SELECT MOD(-25,7)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(-25,7)
----------
-4
SELECT MOD(25.4,7)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(25.4,7)
-----------
4.4
SELECT MOD(25.4,7.2)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(25.4,7.2)
-------------
3.8
SELECT MOD(-25.4,7)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(-25.4,7)
------------
-4.4
SELECT MOD(25,0)
FROM dual;
Output:
MOD(25,0)
----------
25;
SQL MOD() function with distinct
Sample table: customer
To get unique remainder of a division of 'receive_amt' by 'grade' from the 'customer' table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT DISTINCT(MOD(receive_amt,grade))
FROM customer;
Output:
(MOD(RECEIVE_AMT,GRADE))
------------------------
1
2
6000
0
SQL MOD() function with where
Sample table: customer
To get data of 'cust_name', 'opening_amt', 'receive_amt' and remainder of the division of 'opening_amt' by 'receive_amt' from the 'customer' table with following conditions -
1. 'opening_amt' must be more than 'receive_amt',
2. remainder of the division of 'opening_amt' by 'receive_amt' must be more than or equal to 1000,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT cust_name,opening_amt,receive_amt,
MOD(opening_amt,receive_amt)
FROM customer
WHERE opening_amt>receive_amt
AND MOD(opening_amt,receive_amt)>= 1000;
Output:
CUST_NAME OPENING_AMT RECEIVE_AMT MOD(OPENING_AMT,RECEIVE_AMT) ---------------------------------------- ----------- ----------- ---------------------------- Holmes 6000 5000 1000 Yearannaidu 8000 7000 1000 Shilton 10000 7000 3000 Charles 6000 4000 2000 Martin 8000 7000 1000 Ramesh 8000 7000 1000
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition.
Here is a slide presentation which covers the SQL arithmetic functions.
Practice SQL Exercises
- SQL Exercises, Practice, Solution
- SQL Retrieve data from tables [33 Exercises]
- SQL Boolean and Relational operators [12 Exercises]
- SQL Wildcard and Special operators [22 Exercises]
- SQL Aggregate Functions [25 Exercises]
- SQL Formatting query output [10 Exercises]
- SQL Quering on Multiple Tables [8 Exercises]
- FILTERING and SORTING on HR Database [38 Exercises]
- SQL JOINS
- SQL SUBQUERIES
- SQL Union[9 Exercises]
- SQL View[16 Exercises]
- SQL User Account Management [16 Exercise]
- Movie Database
- BASIC queries on movie Database [10 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on movie Database [16 Exercises]
- JOINS on movie Database [24 Exercises]
- Soccer Database
- Introduction
- BASIC queries on soccer Database [29 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on soccer Database [33 Exercises]
- Hospital Database
- Employee Database
- More to come!
Want to improve the above article? Contribute your Notes/Comments/Examples through Disqus.
SQL: Tips of the Day
SQL Server SELECT into existing table.
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
This assumes there's only two columns in dbo.TABLETWO - you need to specify the columns otherwise:
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO (col1, col2) SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
Database: SQL Server
Ref: https://bit.ly/3y6tpA3
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
