SQL FLOOR() function
FLOOR() function
The SQL FLOOR() function rounded up any positive or negative decimal value down to the next least integer value. SQL DISTINCT along with the SQL FLOOR() function is used to retrieve only unique value after rounded down to the next least integer value depending on the column specified.
Syntax:
FLOOR(expression)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| expression | An expression which is a numeric value or numeric data type. The bit data type is not allowed. |
MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and Oracle
All of above platforms support the SQL syntax of FLOOR().
Pictorial presentation of FLOOR() Function
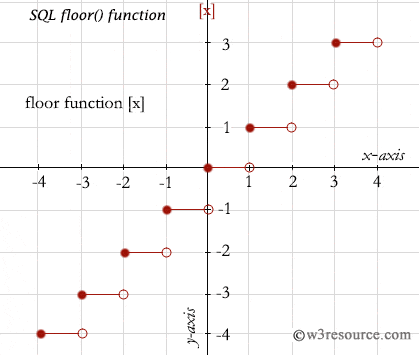
Example:
To get the rounded down to next integer value of 17.36 from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used:
SELECT FLOOR(17.36)
FROM dual;
Output:
FLOOR(17.36)
------------
17
SQL FLOOR() function on negative value
To get the rounded down to next integer value of -17.36 from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT FLOOR(-17.36)
FROM dual;
Output:
FLOOR(-17.36)
-------------
-18
SQL FLOOR() function with distinct
To get the rounded down to next integer value of column 'commission' after multiplying by (-50) from the 'agents' table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT DISTINCT(FLOOR(commission*(-50))) "DISTINCT(FLOOR())",
commission*(-50)
FROM agents;
Output:
DISTINCT(FLOOR()) COMMISSION*(-50)
----------------- ----------------
-6 -5.5
-8 -7.5
-6 -6
-7 -7
-7 -6.5
SQL: Comparing between FLOOR() and CEIL() function
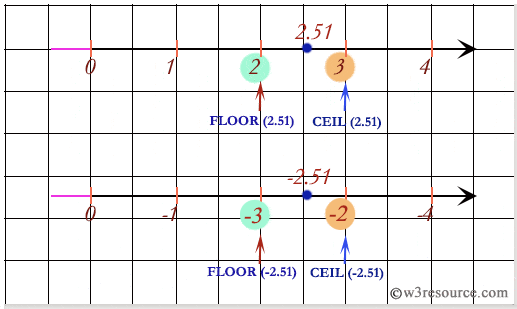
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition.
Here is a slide presentation which covers the SQL arithmetic functions.
Practice SQL Exercises
- SQL Exercises, Practice, Solution
- SQL Retrieve data from tables [33 Exercises]
- SQL Boolean and Relational operators [12 Exercises]
- SQL Wildcard and Special operators [22 Exercises]
- SQL Aggregate Functions [25 Exercises]
- SQL Formatting query output [10 Exercises]
- SQL Quering on Multiple Tables [8 Exercises]
- FILTERING and SORTING on HR Database [38 Exercises]
- SQL JOINS
- SQL SUBQUERIES
- SQL Union[9 Exercises]
- SQL View[16 Exercises]
- SQL User Account Management [16 Exercise]
- Movie Database
- BASIC queries on movie Database [10 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on movie Database [16 Exercises]
- JOINS on movie Database [24 Exercises]
- Soccer Database
- Introduction
- BASIC queries on soccer Database [29 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on soccer Database [33 Exercises]
- Hospital Database
- Employee Database
- More to come!
Want to improve the above article? Contribute your Notes/Comments/Examples through Disqus.
SQL: Tips of the Day
SQL Server SELECT into existing table.
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
This assumes there's only two columns in dbo.TABLETWO - you need to specify the columns otherwise:
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO (col1, col2) SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
Database: SQL Server
Ref: https://bit.ly/3y6tpA3
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
