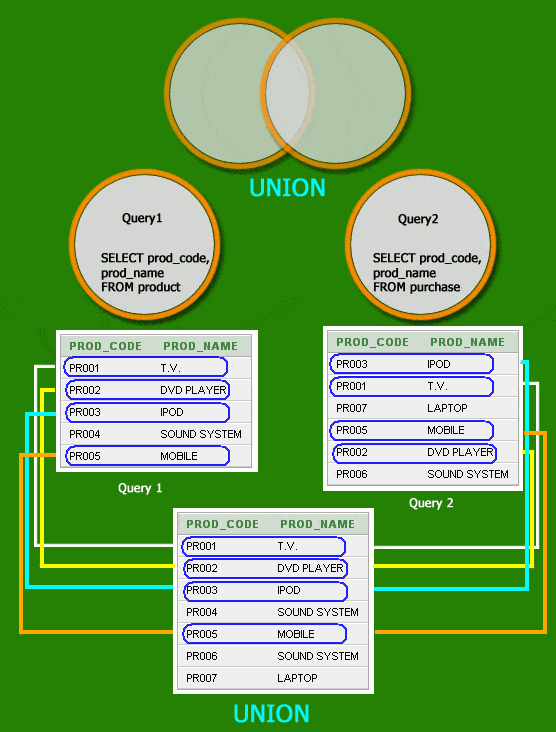
SQL UNION
UNION
The SQL UNION operator combines the results of two or more queries and makes a result set which includes fetched rows from the participating queries in the UNION.
Contents:
Basic rules for combining two or more queries using UNION
Basic rules for combining two or more queries using UNION :
1.) number of columns and order of columns of all queries must be same.
2.) the data types of the columns on involving table in each query must be same or compatible.
3.) Usually returned column names are taken from the first query.
By default the UNION behaves like UNION [DISTINCT] , i.e. eliminated the duplicate rows; however, using ALL keyword with UNION returns all rows, including duplicates.
Difference between SQL JOIN and UNION
1.) The columns of joining tables may be different in JOIN but in UNION the number of columns and order of columns of all queries must be same.
2.) The UNION puts rows from queries after each other( puts vertically ) but JOIN puts the column from queries after each other (puts horizontally), i.e. it makes a cartesian product.
Syntax:
SELECT <column_list>t [INTO ] [FROM ] [WHERE ] [GROUP BY ] [HAVING ] [UNION [ALL] SELECT <column_list> [FROM ] [WHERE ] [GROUP BY ] [HAVING ]...] [ORDER BY ]
The queries are all executed independently but their output is merged.
In the following example, no clause have been added with UNION, so, by default UNION is acting as UNION [DISTINCT] and only the unique rows are available in the result set.
Sample table: product
PROD_CODE PROD_NAME COM_NAME LIFE ---------- --------------- ---------- ---------- PR001 T.V. SONY 7 PR002 DVD PLAYER LG 9 PR003 IPOD PHILIPS 9 PR004 SOUND SYSTEM SONY 8 PR005 MOBILE NOKIA 6
Sample table: purchase
PUR_NO PROD_CODE PROD_NAME COM_NAME PUR_QTY PUR_AMOUNT
---------- ---------- --------------- ---------- ---------- ----------
2 PR001 T.V. SONY 15 450000
1 PR003 IPOD PHILIPS 20 60000
3 PR007 LAPTOP H.P. 6 240000
4 PR005 MOBILE NOKIA 100 300000
5 PR002 DVD PLAYER LG 10 30000
6 PR006 SOUND SYSTEM CREATIVE 8 40000
SQL Code:
SELECT prod_code,prod_name
FROM product
UNION
SELECT prod_code,prod_name
FROM purchase;
Relational Algebra Expression:
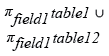
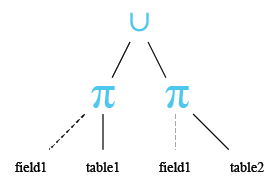
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
PROD_CODE PROD_NAME ---------- --------------- PR001 T.V. PR002 DVD PLAYER PR003 IPOD PR004 SOUND SYSTEM PR005 MOBILE PR006 SOUND SYSTEM PR007 LAPTOP
Pictorial Representation
SQL UNION ALL
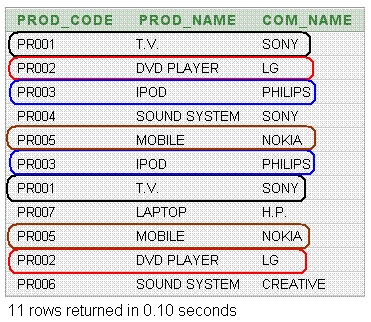
In the following example, the optional clause ALL have been added with UNION for which, all the rows from each query have been available in the result set. Here in the above output, the marking rows are non-unique but it has been displayed. If ignored ALL clause, the marking rows would have come once.
SQL Code:
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM product
UNION ALL
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM purchase;
Relational Algebra Expression:
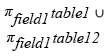
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
SQL UNION ALL using where
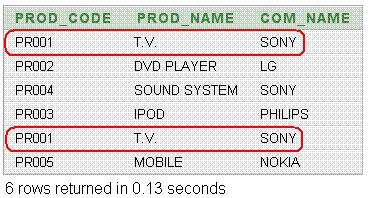
In the following example, the two queries have been set using two different criteria including WHERE clause. So all the retrieve rows (including duplicates) have displayed in the result set. Here in this example, the marking rows are identical, but it has been displayed for the ALL clause along with UNION. If ignored ALL clause the marking rows would have come once.
SQL Code:
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM product
WHERE life>6
UNION ALL
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM purchase
WHERE pur_qty>10
Output:
SQL UNION a table to itself
In the following example, the two queries have been set using two different criteria for the same table. So all the retrieved rows ( including duplicates ) have displayed. Here in this example, the marking rows are identical, but it has been displayed for the ALL clause along with UNION.
SQL Code:
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM purchase
WHERE pur_qty>6
UNION ALL
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,com_name
FROM purchase
WHERE pur_amount>100000
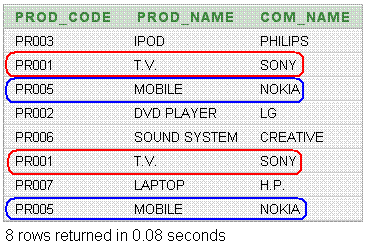
SQL UNION with different column names
In the following example, the two queries have been set using two different criteria and different columns. The different columns in two statements are 'life' and 'pur_qty'. But as the data type are same for both the columns so, result has displayed. Usually returned column names are taken from the first query.
SQL Code:
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,life
FROM product
WHERE life>6
UNION
SELECT prod_code,prod_name,pur_qty
FROM purchase
WHERE pur_qty<20
Output:
PROD_CODE PROD_NAME LIFE ---------- --------------- ---------- PR001 T.V. 7 PR001 T.V. 15 PR002 DVD PLAYER 9 PR002 DVD PLAYER 10 PR003 IPOD 9 PR004 SOUND SYSTEM 8 PR006 SOUND SYSTEM 8 PR007 LAPTOP 6
SQL UNION with Inner Join
In the following example, the union made by two queries. The queries are two inner join statement. In the first query, the join takes place between two tables where the prod_code of both tables are same and in the 2nd query the join take place between two tables where the prod_name of both tables are same.
SQL Code:
SELECT product.prod_code,product.prod_name,
purchase.pur_qty, purchase.pur_amount
FROM product
INNER JOIN purchase
ON product.prod_code =purchase.prod_code
UNION
SELECT product.prod_code,product.prod_name,
purchase.pur_qty, purchase.pur_amount
FROM product
INNER JOIN purchase
ON product.prod_name =purchase.prod_name;
Relational Algebra Expression:
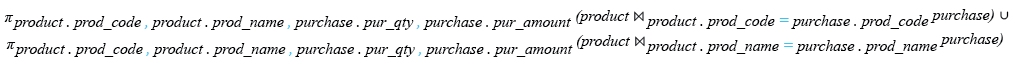
Relational Algebra Tree:
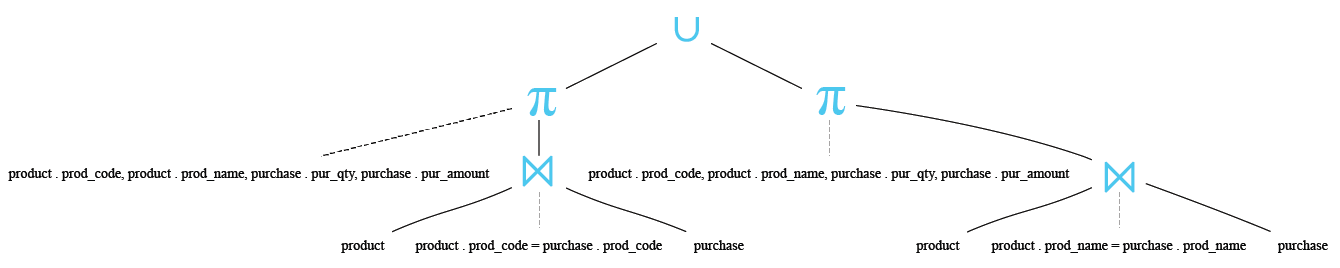
Output:
PROD_CODE PROD_NAME PUR_QTY PUR_AMOUNT ---------- --------------- ---------- ---------- PR001 T.V. 15 450000 PR002 DVD PLAYER 10 30000 PR003 IPOD 20 60000 PR004 SOUND SYSTEM 8 40000 PR005 MOBILE 100 300000
SQL: Union vs Union All
The basic difference between UNION and UNION ALL is, UNION removes duplicate records but UNION ALL does not. Let apply these two commands on two tables table1 and table2.
Rows in table1:
FIELD1
---------
1
4
2
3
Rows in table2 :
FIELD1
----------
2
4
2
1
UNION Example (Removes all duplicate records):
SQL Code:
SELECT field1
FROM table1
UNION
SELECT field1
FROM table2;
Output:
FIELD1
----------
1
2
3
4
UNION ALL Example:
SQL Code:
SELECT field1
FROM table1
UNION ALL
SELECT field1
FROM table2;
Output:
FIELD1
----------
1
4
2
3
2
4
2
1
Practice SQL Exercises
- SQL Exercises, Practice, Solution
- SQL Retrieve data from tables [33 Exercises]
- SQL Boolean and Relational operators [12 Exercises]
- SQL Wildcard and Special operators [22 Exercises]
- SQL Aggregate Functions [25 Exercises]
- SQL Formatting query output [10 Exercises]
- SQL Quering on Multiple Tables [8 Exercises]
- FILTERING and SORTING on HR Database [38 Exercises]
- SQL JOINS
- SQL SUBQUERIES
- SQL Union[9 Exercises]
- SQL View[16 Exercises]
- SQL User Account Management [16 Exercise]
- Movie Database
- BASIC queries on movie Database [10 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on movie Database [16 Exercises]
- JOINS on movie Database [24 Exercises]
- Soccer Database
- Introduction
- BASIC queries on soccer Database [29 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on soccer Database [33 Exercises]
- Hospital Database
- Employee Database
- More to come!
Want to improve the above article? Contribute your Notes/Comments/Examples through Disqus.
Previous: Nested subqueries
Next: Create View
SQL: Tips of the Day
SQL Server SELECT into existing table.
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
This assumes there's only two columns in dbo.TABLETWO - you need to specify the columns otherwise:
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO (col1, col2) SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
Database: SQL Server
Ref: https://bit.ly/3y6tpA3
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework