NumPy: Statistics Exercises, Practice, Solution
NumPy Statistics [14 exercises with solution]
[An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.]
1. Write a Python program to find the maximum and minimum value of a given flattened array. Go to the editor
Expected Output:
Original flattened array:
[[0 1]
[2 3]]
Maximum value of the above flattened array:
3
Minimum value of the above flattened array:
0
Click me to see the sample solution
2. Write a NumPy program to get the minimum and maximum value of a given array along the second axis. Go to the editor
Expected Output:
Original array:
[[0 1]
[2 3]]
Maximum value along the second axis:
[1 3]
Minimum value along the second axis:
[0 2]
Click me to see the sample solution
3. Write a NumPy program to calculate the difference between the maximum and the minimum values of a given array along the second axis. Go to the editor
Expected Output:
Original array:
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
Difference between the maximum and the minimum values of the said array:
[5 5]
Click me to see the sample solution
4. Write a NumPy program to compute the 80th percentile for all elements in a given array along the second axis. Go to the editor
Expected Output:
Original array:
[1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0]
Largest integer smaller or equal to the division of the inputs:
[ 0. 1. 2. 2.]
Click me to see the sample solution
5. Write a NumPy program to compute the median of flattened given array. Go to the editor
Note: First array elements raised to powers from second array
Expected Output:
Original array:
[[ 0 1 2 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8 9 10 11]]
Median of said array:
5.5
Click me to see the sample solution
6. Write a NumPy program to compute the weighted of a given array. Go to the editor
Sample Output:
Original array:
[0 1 2 3 4]
Weighted average of the said array:
2.6666666666666665
Click me to see the sample solution
7. Write a NumPy program to compute the mean, standard deviation, and variance of a given array along the second axis. Go to the editor
Sample output:
Original array:
[0 1 2 3 4 5]
Mean: 2.5
std: 1
variance: 2.9166666666666665
Click me to see the sample solution
8. Write a NumPy program to compute the covariance matrix of two given arrays. Go to the editor
Sample Output:
Original array1:
[0 1 2]
Original array1:
[2 1 0]
Covariance matrix of the said arrays:
[[ 1. -1.]
[-1. 1.]]
Click me to see the sample solution
9. Write a NumPy program to compute cross-correlation of two given arrays. Go to the editor
Sample Output:
Original array1:
[0 1 3]
Original array1:
[2 4 5]
Cross-correlation of the said arrays:
[[2.33333333 2.16666667]
[2.16666667 2.33333333]]
Click me to see the sample solution
10. Write a NumPy program to compute pearson product-moment correlation coefficients of two given arrays. Go to the editor
Sample Output:
Original array1:
[0 1 3]
Original array1:
[2 4 5]
Pearson product-moment correlation coefficients of the said arrays:
[[1. 0.92857143]
[0.92857143 1. ]]
Click me to see the sample solution
11. Write a NumPy program to test element-wise of a given array for finiteness (not infinity or not Not a Number), positive or negative infinity, for NaN, for NaT (not a time), for negative infinity, for positive infinity. Go to the editor
Sample output:
Test element-wise for finiteness (not infinity or not Not a Number):
True
True
False
Test element-wise for positive or negative infinity:
True
False
True
Test element-wise for NaN:
[ True False False]
Test element-wise for NaT (not a time):
[ True False]
Test element-wise for negative infinity:
[1 0 0]
Test element-wise for positive infinity:
[0 0 1]
Click me to see the sample solution
12. Write a Python NumPy program to compute the weighted average along the specified axis of a given flattened array. Go to the editor
From Wikipedia: The weighted arithmetic mean is similar to an ordinary arithmetic mean (the most common type of average), except that instead of each of the data points contributing equally to the final average, some data points contribute more than others. The notion of weighted mean plays a role in descriptive statistics and also occurs in a more general form in several other areas of mathematics.
Sample output:
Original flattened array:
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]]
Weighted average along the specified axis of the above flattened array:
[1.2 4.2 7.2]
Click me to see the sample solution
13. Write a Python program to count number of occurrences of each value in a given array of non-negative integers. Go to the editor
Note: bincount() function count number of occurrences of each value in an array of non-negative integers in the range of the array between the minimum and maximum values including the values that did not occur.
Sample Output:
Original array:
[0, 1, 6, 1, 4, 1, 2, 2, 7]
Number of occurrences of each value in array:
[1 3 2 0 1 0 1 1]
Click me to see the sample solution
14. Write a NumPy program to compute the histogram of nums against the bins. Go to the editor
Sample Output:
nums: [0.5 0.7 1. 1.2 1.3 2.1]
bins: [0 1 2 3]
Result: (array([2, 3, 1], dtype=int64), array([0, 1, 2, 3]))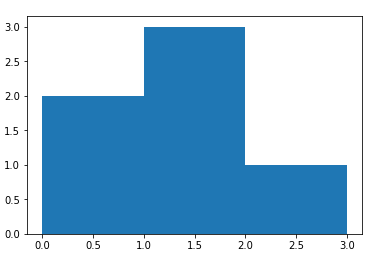
Click me to see the sample solution
Python-Numpy Code Editor:
More to Come !
Do not submit any solution of the above exercises at here, if you want to contribute go to the appropriate exercise page.
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
Python: Tips of the Day
Find current directory and file's directory:
To get the full path to the directory a Python file is contained in, write this in that file:
import os dir_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
(Note that the incantation above won't work if you've already used os.chdir() to change your current working directory, since the value of the __file__ constant is relative to the current working directory and is not changed by an os.chdir() call.)
To get the current working directory use
import os cwd = os.getcwd()
Documentation references for the modules, constants and functions used above:
- The os and os.path modules.
- The __file__ constant
- os.path.realpath(path) (returns "the canonical path of the specified filename, eliminating any symbolic links encountered in the path")
- os.path.dirname(path) (returns "the directory name of pathname path")
- os.getcwd() (returns "a string representing the current working directory")
- os.chdir(path) ("change the current working directory to path")
Ref: https://bit.ly/3fy0R6m
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
