NumPy: splitlines() function
numpy.core.defchararray.splitlines() function
For each element in a given array numpy.core.defchararray.splitlines() function returns a list of the lines in the element, breaking at line boundaries.
Calls str.splitlines element-wise.
Version: 1.15.0
Syntax:
numpy.core.defchararray.splitlines(a, keepends=None)
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| a: array-like of str or unicode | Input an array-like of string or unicode. | Required |
| keepends: bool | Line breaks are not included in the resulting list unless keepends is given and true. | Optional |
Return value:
out [ndarray] Array of list objects.
Note:
The 'chararray' class exists for backwards compatibility with Numarray, it is not recommended for new development. Starting from numpy 1.4, if one needs arrays of strings, it is recommended to use arrays of 'dtype' 'object_', 'string_' or 'unicode_', and use the free functions in the 'numpy.char' module for fast vectorized string operations.
Some methods will only be available if the corresponding string method is available in your version of Python.
The preferred alias for 'defchararray' is 'numpy.char'.
Example-1: numpy.splitlines() function
>>> import numpy as np
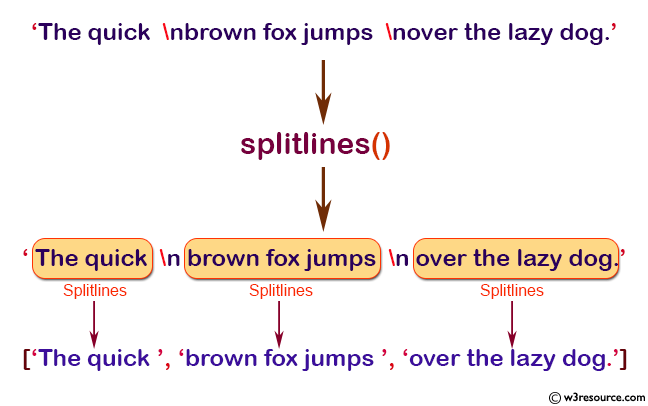
>>> x = np.char.splitlines('The quick \nbrown fox jumps \nover the lazy dog.')
>>> x
array(list(['The quick ', 'brown fox jumps ', 'over the lazy dog.']),
dtype=object)
Pictorial Presentation:
Example-2: numpy.splitlines() function
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.char.splitlines('The quick brown \rfox jumps over \rthe lazy dog.', keepends=None)
>>> x
array(list(['The quick brown ', 'fox jumps over ', 'the lazy dog.']),
dtype=object)
Note: \n or \r is used for breaking at line boundaries.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
