SQL Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic Operators
Arithmetic operators can perform arithmetical operations on numeric operands involved. Arithmetic operators are addition(+), subtraction(-), multiplication(*) and division(/). The + and - operators can also be used in date arithmetic.
| Operator | Meaning | Operates on |
|---|---|---|
| + (Add) | Addition | Numeric value |
| - (Subtract) | Subtraction | Numeric value |
| * (Multiply) | Multiplication | Numeric value |
| / (Divide) | Division | Numeric value |
| % (Modulo) | Returns the integer remainder of a division. For example, 17 % 5 = 2 because the remainder of 17 divided by 5 is 2. | Numeric value |
Syntax:
SELECT <Expression>[arithmetic operator]<expression>... FROM [table_name] WHERE [expression];
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Expression | Expression made up of a single constant, variable, scalar function, or column name and can also be the pieces of a SQL query that compare values against other values or perform arithmetic calculations. |
| arithmetic operator | Plus(+), minus(-), multiply(*), and divide(/). |
| table_name | Name of the table. |
Contents:
Example: SQL Arithmetic Operators
This is a simple example of using SQL arithmetic operators:
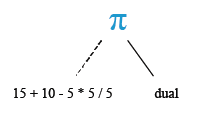
SELECT 15+10-5*5/5 FROM dual;
Relational Algebra Expression:
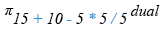
Relational Algebra Tree:
SQL plus (+) operator
The SQL plus (+) operator is used to add two or more expressions or numbers.
Example:
Sample table: customer
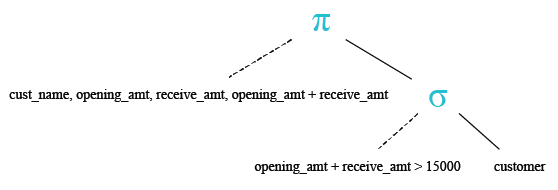
To get data of 'cust_name', 'opening_amt', 'receive_amt', ('opening_amt' + 'receive_amt') from the 'customer' table with following condition -
1. sum of 'opening_amt' and 'receive_amt' is greater than 15000,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT cust_name, opening_amt,
receive_amt, (opening_amt + receive_amt)
FROM customer
WHERE (opening_amt + receive_amt)>15000;
Output:
CUST_NAME OPENING_AMT RECEIVE_AMT (OPENING_AMT+RECEIVE_AMT) ---------------------------------------- ----------- ----------- ------------------------- Sasikant 7000 11000 18000 Ramanathan 7000 11000 18000 Avinash 7000 11000 18000 Shilton 10000 7000 17000 Rangarappa 8000 11000 19000 Venkatpati 8000 11000 19000 Sundariya 7000 11000 18000
Relational Algebra Expression:
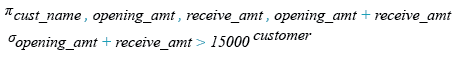
Relational Algebra Tree:
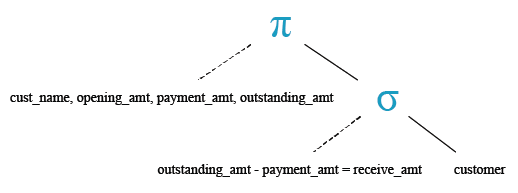
SQL minus (-) operator
The SQL minus (-) operator is used to subtract one expression or number from another expression or number.
Example:
To get data of 'cust_name', 'opening_amount', 'payment_amount' and 'oustanding_amount' from the 'customer' table with following condition -
1. 'outstanding_amt' - 'payment_amt' is equal to the 'receive_amt',
the following SQL statement can be used:/p>
SELECT cust_name,opening_amt, payment_amt, outstanding_amt
FROM customer
WHERE(outstanding_amt-payment_amt)=receive_amt;
Output:
CUST_NAME OPENING_AMT PAYMENT_AMT OUTSTANDING_AMT ---------------------------------------- ----------- ----------- --------------- Stuart 6000 3000 11000
Relational Algebra Expression:
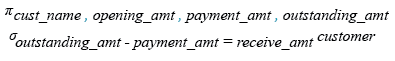
Relational Algebra Tree:
SQL multiply ( * ) operator
The SQL multiply ( * ) operator is used to multiply two or more expressions or numbers.
Example:
Sample table: agents
To get data of 'agent_code', 'agent_name', 'working_area' and ('commission'*2) from the 'agents' table with following condition -
1. two times of the default 'commission' is greater than 0.25,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT agent_code, agent_name,
working_area, (commission*2)
FROM agents
WHERE (commission*2)>0.25;
Output:
AGENT_ AGENT_NAME WORKING_AREA (COMMISSION*2) ------ ---------------------------------------- ----------------------------------- -------------- A003 Alex London .26 A001 Subbarao Bangalore .28 A007 Ramasundar Bangalore .3 A011 Ravi Kumar Bangalore .3 A010 Santakumar Chennai .28 A005 Anderson Brisban .26 A006 McDen London .3 A004 Ivan Torento .3
Relational Algebra Expression:

Relational Algebra Tree:
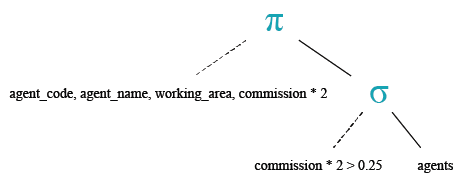
SQL divide ( / ) operator
The SQL divide ( / ) operator is used to divide one expressions or numbers by another.
Example:
To get data of 'cust_name', 'opening_amt', 'receive_amt', 'outstanding_amt' and ('receive_amt'*5/ 100) as a column heading 'commission' from the customer table with following condition -
1. 'outstanding_amt' is less than or equal to 4000,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT cust_name, opening_amt, receive_amt,
outstanding_amt, (receive_amt*5/ 100) commission
FROM customer
WHERE outstanding_amt<=4000;
Output:
CUST_NAME OPENING_AMT RECEIVE_AMT OUTSTANDING_AMT COMMISSION ---------------------------------------- ----------- ----------- --------------- ---------- Holmes 6000 5000 4000 250 Bolt 5000 7000 3000 350 Karl 4000 6000 3000 300 Steven 5000 7000 3000 350
SQL modulo ( % ) operator
The SQL MODULO operator returns the remainder (an integer) of the division.
Example:To get the modulus of a division of 150 by 7 from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT 150%7;
Output:

Practice SQL Exercises
- SQL Exercises, Practice, Solution
- SQL Retrieve data from tables [33 Exercises]
- SQL Boolean and Relational operators [12 Exercises]
- SQL Wildcard and Special operators [22 Exercises]
- SQL Aggregate Functions [25 Exercises]
- SQL Formatting query output [10 Exercises]
- SQL Quering on Multiple Tables [8 Exercises]
- FILTERING and SORTING on HR Database [38 Exercises]
- SQL JOINS
- SQL SUBQUERIES
- SQL Union[9 Exercises]
- SQL View[16 Exercises]
- SQL User Account Management [16 Exercise]
- Movie Database
- BASIC queries on movie Database [10 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on movie Database [16 Exercises]
- JOINS on movie Database [24 Exercises]
- Soccer Database
- Introduction
- BASIC queries on soccer Database [29 Exercises]
- SUBQUERIES on soccer Database [33 Exercises]
- Hospital Database
- Employee Database
- More to come!
Want to improve the above article? Contribute your Notes/Comments/Examples through Disqus.
SQL: Tips of the Day
SQL Server SELECT into existing table.
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
This assumes there's only two columns in dbo.TABLETWO - you need to specify the columns otherwise:
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO (col1, col2) SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
Database: SQL Server
Ref: https://bit.ly/3y6tpA3
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
