SQL exercises on employee Database: List the manager no and the number of employees working for those managers in ascending order on manager id
SQL employee Database: Exercise-96 with Solution
[An editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.]
96. From the following table, write a SQL query to list the managers and number of employees work under them. Sort the result set in ascending order on manager. Return manager ID and number of employees under them.
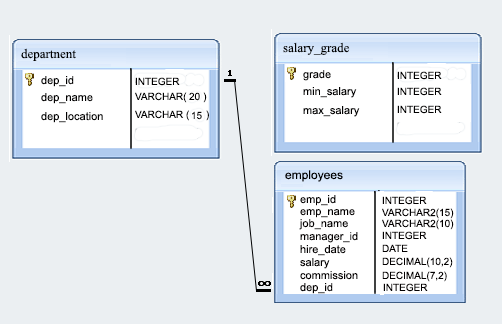
Sample table: employees
Sample Solution:
SELECT w.manager_id,
count(*)
FROM employees w,
employees m
WHERE w.manager_id = m.emp_id
GROUP BY w.manager_id
ORDER BY w.manager_id ASC;
Sample Output:
manager_id | count
------------+-------
65646 | 2
66928 | 5
67832 | 1
67858 | 1
68319 | 3
69062 | 1
(6 rows)
Relational Algebra Expression:
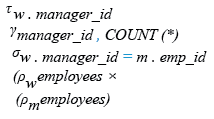
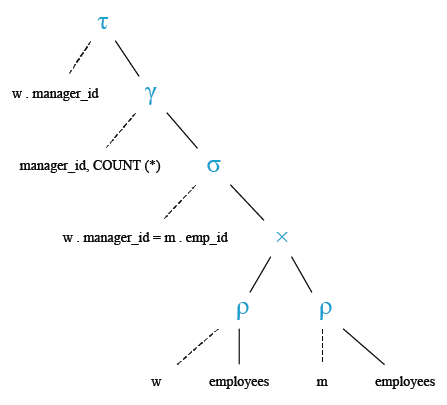
Relational Algebra Tree:
Practice Online
Sample Database: employee
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: From the following table, write a SQL query to find those employees whose salary is in the range minimum and maximum salary (Begin and end values are included.). Return employee ID, name, salary and grade.
Next: From the following table, write a SQL query to count the number of employees of each designation in each department. Return department id, job name and number of employees.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
SQL: Tips of the Day
SQL Server SELECT into existing table.
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
This assumes there's only two columns in dbo.TABLETWO - you need to specify the columns otherwise:
INSERT INTO dbo.TABLETWO (col1, col2) SELECT col1, col2 FROM dbo.TABLEONE WHERE col3 LIKE @search_key
Database: SQL Server
Ref: https://bit.ly/3y6tpA3
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
