NumPy: Calculate the QR decomposition of a given matrix
NumPy: Linear Algebra Exercise-13 with Solution
Write a NumPy program to calculate the QR decomposition of a given matrix.
From Wikipedia: In linear algebra, a QR decomposition (also called a QR factorization) of a matrix is a decomposition of a matrix A into a product A = QR of an orthogonal matrix Q and an upper triangular matrix R. QR decomposition is often used to solve the linear least squares problem and is the basis for a particular eigenvalue algorithm, the QR algorithm.
Square matrix
Any real square matrix A may be decomposed as
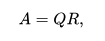
where Q is an orthogonal matrix (its columns are orthogonal unit vectors meaning {\displaystyle Q^{\textsf {T}}Q=QQ^{\textsf {T}}=I} {\displaystyle Q^{\textsf {T}}Q=QQ^{\textsf {T}}=I}) and R is an upper triangular matrix (also called right triangular matrix). If A is invertible, then the factorization is unique if we require the diagonal elements of R to be positive.
If instead A is a complex square matrix, then there is a decomposition A = QR where Q is a unitary matrix (so {\displaystyle Q^{*}Q=QQ^{*}=I} {\displaystyle Q^{*}Q=QQ^{*}=I}).
If A has n linearly independent columns, then the first n columns of Q form an orthonormal basis for the column space of A. More generally, the first k columns of Q form an orthonormal basis for the span of the first k columns of A for any 1 ≤ k ≤ n.[1] The fact that any column k of A only depends on the first k columns of Q is responsible for the triangular form of R.[1]
Sample Solution :
Python Code :
import numpy as np
m = np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
print("Original matrix:")
print(m)
result = np.linalg.qr(m)
print("Decomposition of the said matrix:")
print(result)
Sample Output:
Original matrix:
[[1 2]
[3 4]]
Decomposition of the said matrix:
(array([[-0.31622777, -0.9486833 ],
[-0.9486833 , 0.31622777]]), array([[-3.16227766, -4.42718872],
[ 0. , -0.63245553]]))
Python-Numpy Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Write a NumPy program to compute the inverse of a given matrix.
Next: Write a NumPy program to compute the condition number of a given matrix.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
Python: Tips of the Day
Find current directory and file's directory:
To get the full path to the directory a Python file is contained in, write this in that file:
import os dir_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
(Note that the incantation above won't work if you've already used os.chdir() to change your current working directory, since the value of the __file__ constant is relative to the current working directory and is not changed by an os.chdir() call.)
To get the current working directory use
import os cwd = os.getcwd()
Documentation references for the modules, constants and functions used above:
- The os and os.path modules.
- The __file__ constant
- os.path.realpath(path) (returns "the canonical path of the specified filename, eliminating any symbolic links encountered in the path")
- os.path.dirname(path) (returns "the directory name of pathname path")
- os.getcwd() (returns "a string representing the current working directory")
- os.chdir(path) ("change the current working directory to path")
Ref: https://bit.ly/3fy0R6m
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
