Python File I/O: Takes a text file as input and returns the number of words of a given text file
Python File I/O: Exercise-18 with Solution
Write a Python program that takes a text file as input and returns the number of words of a given text file.
Note: Some words can be separated by a comma with no space.
words.txt: Write a Python program that accept some words and count the number of distinct words. Print the number of distinct words and number of occurrences for each distinct word according to their appearance.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
def count_words(filepath):
with open(filepath) as f:
data = f.read()
data.replace(",", " ")
return len(data.split(" "))
print(count_words("words.txt"))
Sample Output:
33
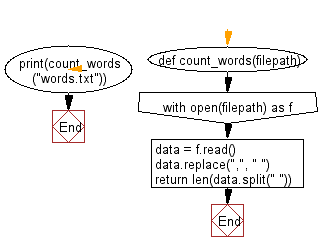
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous: Write a Python program to remove newline characters from a file.
Next: Write a Python program to extract characters from various text files and puts them into a list.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
Python: Tips of the Day
Find current directory and file's directory:
To get the full path to the directory a Python file is contained in, write this in that file:
import os dir_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
(Note that the incantation above won't work if you've already used os.chdir() to change your current working directory, since the value of the __file__ constant is relative to the current working directory and is not changed by an os.chdir() call.)
To get the current working directory use
import os cwd = os.getcwd()
Documentation references for the modules, constants and functions used above:
- The os and os.path modules.
- The __file__ constant
- os.path.realpath(path) (returns "the canonical path of the specified filename, eliminating any symbolic links encountered in the path")
- os.path.dirname(path) (returns "the directory name of pathname path")
- os.getcwd() (returns "a string representing the current working directory")
- os.chdir(path) ("change the current working directory to path")
Ref: https://bit.ly/3fy0R6m
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
