Python Challenges: Get a dictionary mapping keys to huffman codes for a frequency table mapping keys to frequencies
Python Challenges - 1: Exercise-58 with Solution
From Wikipedia,
In computer science and information theory, a Huffman code is a particular type of optimal prefix code that is commonly used for lossless data compression. The process of finding or using such a code proceeds by means of Huffman coding, an algorithm developed by David A. Huffman while he was a Sc.D. student at MIT, and published in the 1952 paper "A Method for the Construction of Minimum-Redundancy Codes".
Write a Python program to get a dictionary mapping keys to huffman codes for a frequency table mapping keys to frequencies.
Sample Solution:
Python Code:
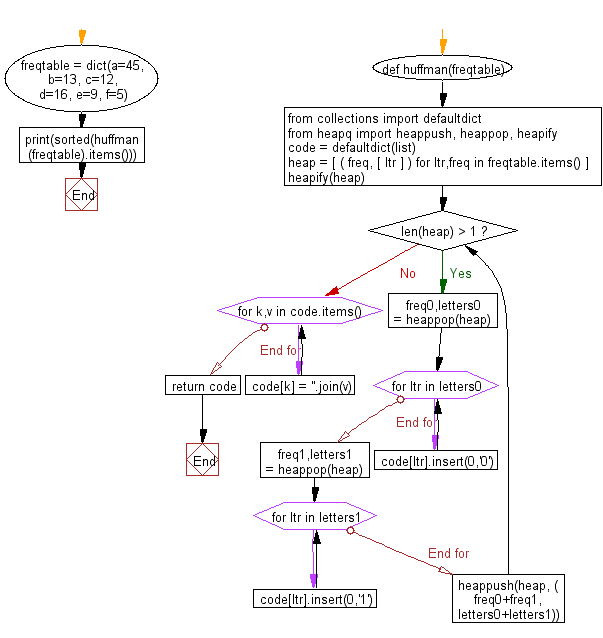
def huffman(freqtable):
# Ref.: https://bit.ly/3cWJD22
from collections import defaultdict
from heapq import heappush, heappop, heapify
# mapping of letters to codes
code = defaultdict(list)
# Using a heap makes it easy to pull items with lowest frequency.
# Items in the heap are tuples containing a list of letters and the
# combined frequencies of the letters in the list.
heap = [ ( freq, [ ltr ] ) for ltr,freq in freqtable.items() ]
heapify(heap)
# Reduce the heap to a single item by combining the two items
# with the lowest frequencies.
while len(heap) > 1:
freq0,letters0 = heappop(heap)
for ltr in letters0:
code[ltr].insert(0,'0')
freq1,letters1 = heappop(heap)
for ltr in letters1:
code[ltr].insert(0,'1')
heappush(heap, ( freq0+freq1, letters0+letters1))
for k,v in code.items():
code[k] = ''.join(v)
return code
freqtable = dict(a=45, b=13, c=12, d=16, e=9, f=5)
print(sorted(huffman(freqtable).items()))
Sample Output:
[('a', '0'), ('b', '101'), ('c', '100'), ('d', '111'), ('e', '1101'), ('f', '1100')]
Flowchart:
Python Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
Previous: Write a Python program to generate list with 'width'-bit gray code.
Next: Write a Python program to compute the sum of the numbers on the diagonals in a 1001 by 1001 spiral formed.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
Python: Tips of the Day
Find current directory and file's directory:
To get the full path to the directory a Python file is contained in, write this in that file:
import os dir_path = os.path.dirname(os.path.realpath(__file__))
(Note that the incantation above won't work if you've already used os.chdir() to change your current working directory, since the value of the __file__ constant is relative to the current working directory and is not changed by an os.chdir() call.)
To get the current working directory use
import os cwd = os.getcwd()
Documentation references for the modules, constants and functions used above:
- The os and os.path modules.
- The __file__ constant
- os.path.realpath(path) (returns "the canonical path of the specified filename, eliminating any symbolic links encountered in the path")
- os.path.dirname(path) (returns "the directory name of pathname path")
- os.getcwd() (returns "a string representing the current working directory")
- os.chdir(path) ("change the current working directory to path")
Ref: https://bit.ly/3fy0R6m
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
