PHP Exercises: Create a new function that composes multiple functions into a single callable
PHP: Exercise-98 with Solution
Write a PHP program to create a new function that composes multiple functions into a single callable.
Sample Solution: -
PHP Code:
<?php
//Licence: https://bit.ly/2CFA5XY
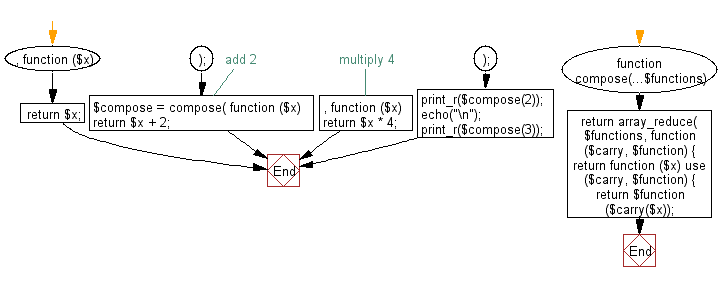
function compose(...$functions)
{
return array_reduce(
$functions,
function ($carry, $function) {
return function ($x) use ($carry, $function) {
return $function($carry($x));
};
},
function ($x) {
return $x;
}
);
}
$compose = compose(
// add 2
function ($x) {
return $x + 2;
},
// multiply 4
function ($x) {
return $x * 4;
}
);
print_r($compose(2));
echo("\n");
print_r($compose(3));
?>
Sample Output:
16 20
Flowchart:
PHP Code Editor:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
Previous:Write a PHP program to decapitalize the first letter of the string and then adds it with rest of the string.
Next: Write a PHP program to memoize a given function results in memory.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
PHP: Tips of the Day
How to Sort Multi-dimensional Array by Value?
Try a usort, If you are still on PHP 5.2 or earlier, you'll have to define a sorting function first:
Example:
function sortByOrder($a, $b) {
return $a['order'] - $b['order'];
}
usort($myArray, 'sortByOrder');
Starting in PHP 5.3, you can use an anonymous function:
usort($myArray, function($a, $b) {
return $a['order'] - $b['order'];
});
And finally with PHP 7 you can use the spaceship operator:
usort($myArray, function($a, $b) {
return $a['order'] <=> $b['order'];
});
To extend this to multi-dimensional sorting, reference the second/third sorting elements if the first is zero - best explained below. You can also use this for sorting on sub-elements.
usort($myArray, function($a, $b) {
$retval = $a['order'] <=> $b['order'];
if ($retval == 0) {
$retval = $a['suborder'] <=> $b['suborder'];
if ($retval == 0) {
$retval = $a['details']['subsuborder'] <=> $b['details']['subsuborder'];
}
}
return $retval;
});
If you need to retain key associations, use uasort() - see comparison of array sorting functions in the manual
Ref : https://bit.ly/3i77vCC
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
