Java Exercises: Create the first twenty Hamming numbers
Java Numbers: Exercise-27 with Solution
Write a Java program to create the first twenty Hamming numbers.
Pictorial Presentation:
In computer science, regular numbers are often called Hamming numbers, Hamming Numbers are numbers whose only prime factors are 2, 3 and 5.
The first few hamming numbers are :
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 18, 20, 24, 25, 27, 30, 32
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// https://rosettacode.org/
import java.math.BigInteger;
public class Exercise28 {
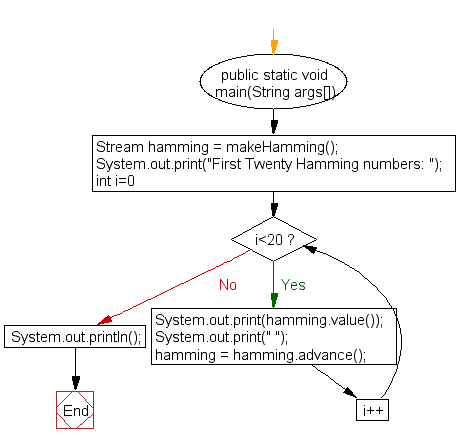
public static void main(String args[])
{
Stream hamming = makeHamming();
System.out.print("First Twenty Hamming numbers: ");
for (int i=0; i<20; i++) {
System.out.print(hamming.value());
System.out.print(" ");
hamming = hamming.advance();
}
System.out.println();
}
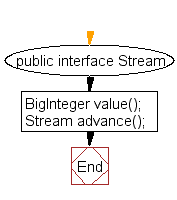
public interface Stream
{
BigInteger value();
Stream advance();
}
public static class MultStream implements Stream
{
MultStream(int mult)
{ m_mult = BigInteger.valueOf(mult); }
MultStream setBase(Stream s)
{ m_base = s; return this; }
public BigInteger value()
{ return m_mult.multiply(m_base.value()); }
public Stream advance()
{ return setBase(m_base.advance()); }
private final BigInteger m_mult;
private Stream m_base;
}
private final static class RegularStream implements Stream
{
RegularStream(Stream[] streams, BigInteger val)
{
m_streams = streams;
m_val = val;
}
public BigInteger value()
{ return m_val; }
public Stream advance()
{
// memoized value for the next stream instance.
if (m_advance != null) { return m_advance; }
int minidx = 0 ;
BigInteger next = nextStreamValue(0);
for (int i=1; i<m_streams.length; i++) {
BigInteger v = nextStreamValue(i);
if (v.compareTo(next) < 0) {
next = v;
minidx = i;
}
}
RegularStream ret = new RegularStream(m_streams, next);
// memoize the value!
m_advance = ret;
m_streams[minidx].advance();
return ret;
}
private BigInteger nextStreamValue(int streamidx)
{
// skip past duplicates in the streams we're merging.
BigInteger ret = m_streams[streamidx].value();
while (ret.equals(m_val)) {
m_streams[streamidx] = m_streams[streamidx].advance();
ret = m_streams[streamidx].value();
}
return ret;
}
private final Stream[] m_streams;
private final BigInteger m_val;
private RegularStream m_advance = null;
}
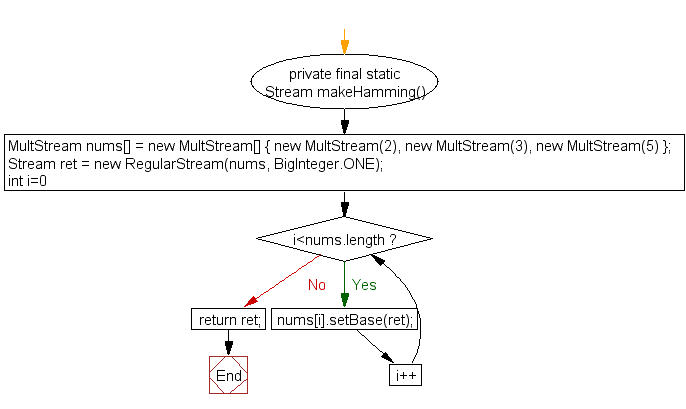
private final static Stream makeHamming()
{
MultStream nums[] = new MultStream[] {
new MultStream(2),
new MultStream(3),
new MultStream(5)
};
Stream ret = new RegularStream(nums, BigInteger.ONE);
for (int i=0; i<nums.length; i++) {
nums[i].setBase(ret);
}
return ret;
}
}
Sample Output:
First Twenty Hamming numbers: 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 12 15 16 18 20 24 25 27 30 32 36
Flowchart:
interface Stream :
MultStream implements Stream :
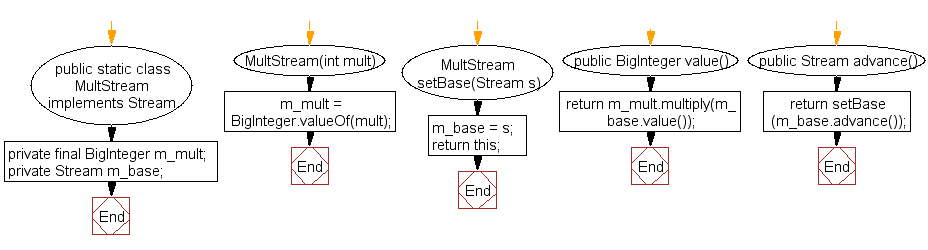
RegularStream implements Stream :
Stream makeHamming :
Java Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
Previous: Write a Program in Java to check whether a number is a Keith Number or not.
Next: Write a Program in Java to check whether a number is an Armstrong Number or not.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
Java: Tips of the Day
How to sort an ArrayList?
Collections.sort(testList); Collections.reverse(testList);
That will do what you want. Remember to import Collections though!
Ref: https://bit.ly/32urdSe
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework

