C Exercises: Read month number and display number of days for that month
C Conditional Statement: Exercise-24 with Solution
Write a program in C to read any Month Number in integer and display the number of days for this month.
Pictorial Presentation:

Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
void main()
{
int monno;
char monnm[15];
printf("Input Month No : ");
scanf("%d",&monno);
switch(monno)
{
case 1:
case 3:
case 5:
case 7:
case 8:
case 10:
case 12:
printf("Month have 31 days. \n");
break;
case 2:
printf("The 2nd month is a February and have 28 days. \n");
printf("in leap year The February month Have 29 days.\n");
break;
case 4:
case 6:
case 9:
case 11:
printf("Month have 30 days. \n");
break;
default:
printf("invalid Month number.\nPlease try again ....\n");
break;
}
}
Sample Output:
Input Month No : 7 Month have 31 days.
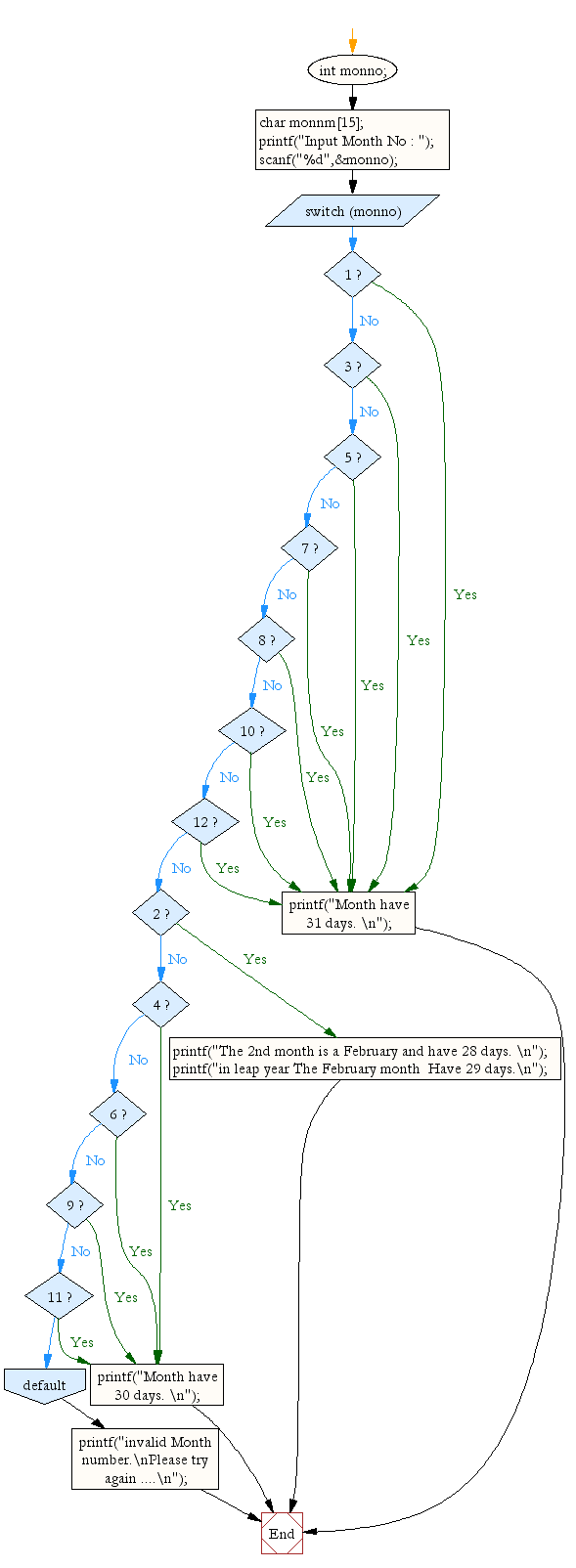
Flowchart:
C Programming Code Editor:
Improve this sample solution and post your code through Disqus.
Previous: Write a program in C to read any Month Number in integer and display Month name in the word.
Next: Next: Write a program in C which is a Menu-Driven Program to compute the area of the various geometrical shape.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
C Programming: Tips of the Day
Static variable inside of a function in C
The scope of variable is where the variable name can be seen. Here, x is visible only inside function foo().
The lifetime of a variable is the period over which it exists. If x were defined without the keyword static, the lifetime would be from the entry into foo() to the return from foo(); so it would be re-initialized to 5 on every call.
The keyword static acts to extend the lifetime of a variable to the lifetime of the programme; e.g. initialization occurs once and once only and then the variable retains its value - whatever it has come to be - over all future calls to foo().
Ref : https://bit.ly/3fOq7XP
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
