C Exercises: Calculate the sum of the two integers
C Basic Declarations and Expressions: Exercise-9 with Solution
Write a C program that accepts two integers from the user and calculate the sum of the two integers.
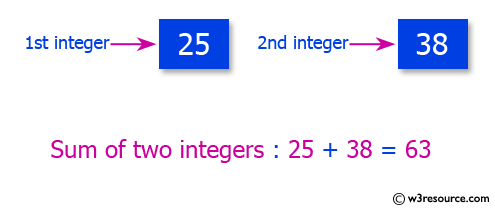
Pictorial Presentation:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int x, y, sum;
printf("\nInput the first integer: ");
scanf("%d", &x);
printf("\nInput the second integer: ");
scanf("%d", &y);
sum = x + y;
printf("\nSum of the above two integers = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input the first integer: 25
Input the second integer: 38
Sum of the above two integers = 63
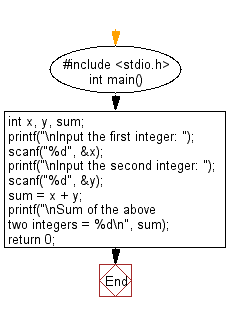
Flowchart:
C Programming Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
Previous: Write a C program to convert specified days into years, weeks and days.
Next: Write a C program that accepts two integers from the user and calculate the product of the two integers.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
C Programming: Tips of the Day
Static variable inside of a function in C
The scope of variable is where the variable name can be seen. Here, x is visible only inside function foo().
The lifetime of a variable is the period over which it exists. If x were defined without the keyword static, the lifetime would be from the entry into foo() to the return from foo(); so it would be re-initialized to 5 on every call.
The keyword static acts to extend the lifetime of a variable to the lifetime of the programme; e.g. initialization occurs once and once only and then the variable retains its value - whatever it has come to be - over all future calls to foo().
Ref : https://bit.ly/3fOq7XP
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
