C Exercises: Find the number of combinations that satisfy p + q + r + s = n
C Basic Declarations and Expressions: Exercise-147 with Solution
Write a C program to find the number of combinations that satisfy p + q + r + s = n where n is a given number <= 4000 and p, q, r, s in the range of 0 to 1000.
Sample Solution:
C Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define check_num(x) (x>0?x:0)
int n,result,x;
int main(void){
printf("Input a positive integer:\n");
scanf("%d",&n);
result=0;
for(x=check_num(n-2000);x<=2000 && n>=x;x++){
result+=(1001-abs(1000-(n-x)))*(1001-abs(1000-x));
}
printf("\nNumber of combinations of p,q,r,s:\n");
printf("%d\n",result);
return 0;
}
Sample Output:
Input a positive integer: 25 Number of combinations of p,q,r,s: 3276
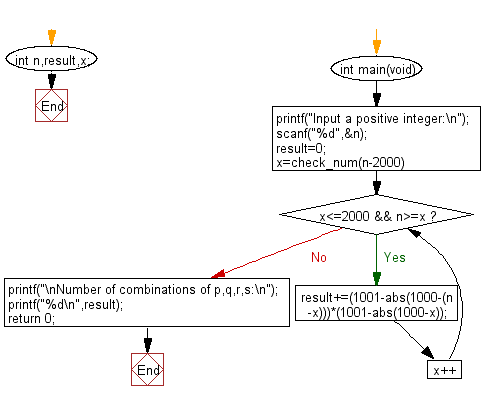
Flowchart:
C programming Code Editor:
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
Previous: Write a C program to extract words of 3 to 6 characters length from a given sentence not more than 1024 characters.
Next: Write a C program, which adds up columns and rows of given table as shown in the following figure.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
C Programming: Tips of the Day
Static variable inside of a function in C
The scope of variable is where the variable name can be seen. Here, x is visible only inside function foo().
The lifetime of a variable is the period over which it exists. If x were defined without the keyword static, the lifetime would be from the entry into foo() to the return from foo(); so it would be re-initialized to 5 on every call.
The keyword static acts to extend the lifetime of a variable to the lifetime of the programme; e.g. initialization occurs once and once only and then the variable retains its value - whatever it has come to be - over all future calls to foo().
Ref : https://bit.ly/3fOq7XP
- New Content published on w3resource:
- HTML-CSS Practical: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Java Regular Expression: Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Scala Programming Exercises, Practice, Solution
- Python Itertools exercises
- Python Numpy exercises
- Python GeoPy Package exercises
- Python Pandas exercises
- Python nltk exercises
- Python BeautifulSoup exercises
- Form Template
- Composer - PHP Package Manager
- PHPUnit - PHP Testing
- Laravel - PHP Framework
- Angular - JavaScript Framework
- Vue - JavaScript Framework
- Jest - JavaScript Testing Framework
